CLIENT SERVER MODEL - DBMS
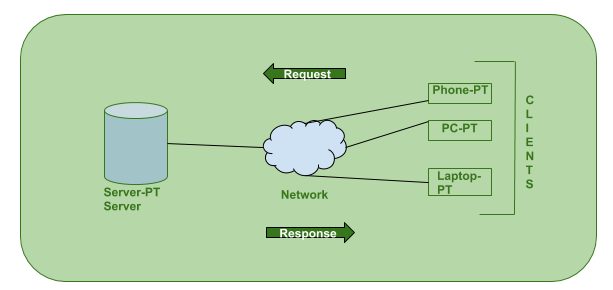
The Client-Server model is a distributed architecture system that divides the task between the servers and clients. Here, when the client sends a request to the server through the internet, the server accepts the requested process and delivers the requested data packets back to the client.
The browser interacts with server as:- User enters the URL(Uniform Resource Locator) of the website. The browser then requests the DNS (Domain Name System) server.
- DNS Server looks up for the address of the WEB Server.
- DNS Server responds with the IP Address of the WEB Server.
- Browser sends over an HTTP/HTTPS request to the WEB Server's IP
- Server sends over the necessary files of the websites.
- Browsers then renders the files and website is displayed.
Advantages:- Centralized System
- Cost Efficient
- Data recovery
- Capacity of client and servers can be changed
Disadvantages:- Clients are prone to virus if present in server or uploaded into the server
- Servers are prone to Denial of Service (DOS) attacks
- Data packets may be spoofed or removed during transmission
- Phishing or capturing login credentials or other useful information of
the user are common and MITM(Man in the Middle) attacks are common.
Source: GeeksForGeeks
Comments
Post a Comment